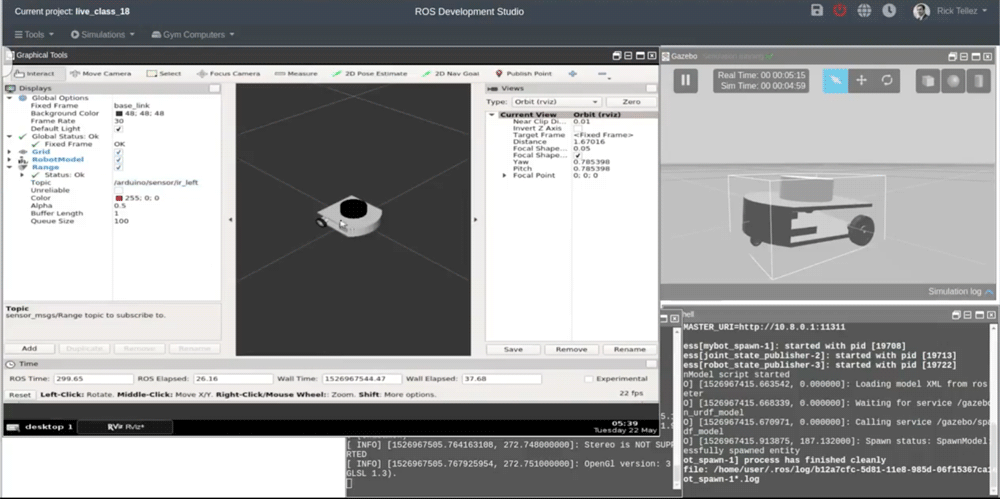
In this video, we are answering a question about why the range sensor plugin for Gazebo is not detecting obstacles. The answer to that problem will surprise you !!! (ha, ha, ha).
In this posting, we will go through a demo of laser data visualization
NOTE: This article assumes that the audience is familiar with the following:
- Running scripts on the terminal
- Ros filesystem layout (what goes where
launchdir,srcdir etc) - RDS Environment (How to launch a project, how to navigate the directories.
Step – 1. Creating a new project
- Head to https://rds.theconstructsim.com/ (if not there already)
- Create a new project. Choose an informative name and add some description in the description field.
- Load the project. (This can take a few moments to a minute depending on your internet)
- Run the
IDEfrom theTools menuand verify the filesystem layout it should have a similar structure
root
├── ai_ws
├── catkin_ws
│ ├── build
│ ├── devel
│ └── src
├── notebook_ws
│ ├── default.ipynb
│ └── images
└── simulation_ws
├── build
├── devel
└── src
Step – 2. Cloning the existing source
- Start the shell, browse to
catkin_ws/src - Clone the git repository located at https://github.com/erenaud3/fakeLaserScan (more information on cloning a git-repo is available here
$ git clone https://github.com/erenaud3/fakeLaserScan
- The filesystem tree should look like the following
root
├── ai_ws
├── catkin_ws
│ ├── build
│ ├── devel
│ └── src
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ └── fakeLaserScan
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ ├── launch
│ │ └── fakeLaserScan.launch
│ ├── package.xml
│ ├── README.md
│ └── src
│ ├── fakeLaserScan.cpp
│ ├── listener.cpp
│ └── talker.cpp
├── notebook_ws
│ ├── default.ipynb
│ └── images
└── simulation_ws
├── build
├── devel
└── src
Step – 3. Briefly skim through the code and run it
- First, we go through the contents of package.xml (located inside the fakeLaserScan directory) which has the following content
(NOTE comments are removed in this reproduced code snippet for brevity)
<?xml version="1.0"?> <package> <name>beginner_tutorials</name> <version>0.0.0</version> <description>The beginner_tutorials package</description> <maintainer email="user@todo.todo">user</maintainer> <license>TODO</license> <buildtool_depend>catkin</buildtool_depend> <build_depend>roscpp</build_depend> <build_depend>rospy</build_depend> <build_depend>sensor_msgs</build_depend> <build_depend>std_msgs</build_depend> <build_export_depend>roscpp</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>rospy</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>sensor_msgs</build_export_depend> <build_export_depend>std_msgs</build_export_depend> <exec_depend>roscpp</exec_depend> <exec_depend>rospy</exec_depend> <exec_depend>sensor_msgs</exec_depend> <exec_depend>std_msgs</exec_depend> <export> </export> </package>
This file contains various pieces of information about the project such as the package dependencies (roscpp, rospy, sensor_msgs, std_msgs) project name, version, license, maintainer etc. Some of this information is vital for building the project (like the dependencies). While other information is important from the perspective of sharing one’s work with the community.
In the given contents of the package.xml file, we notice that the project name specified in the file (beginner_tutorials) is different from the directory name (fakeLaserScanner). While this will not cause the project to crash but it is inconsistent with the project naming guideline.
Next, we take a look at the code inside fakeLaserScan.cpp
#include <ros/ros.h>
#include <sensor_msgs/LaserScan.h>
int main(int argc, char** argv){
ros::init(argc, argv, "fake_laser_scan_publisher");
ros::NodeHandle n;
ros::Publisher scan_pub = n.advertise<sensor_msgs::LaserScan>("fakeScan", 50);
unsigned int num_readings = 100;
double laser_frequency = 40;
double ranges[num_readings];
double intensities[num_readings];
int count = 0;
ros::Rate r(1.0);
while(n.ok()){
//generate some fake data for our laser scan
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < num_readings; ++i){
ranges[i] = 5;
intensities[i] = 100 + count;
}
ros::Time scan_time = ros::Time::now();
//populate the LaserScan message
sensor_msgs::LaserScan scan;
scan.header.stamp = scan_time;
scan.header.frame_id = "fake_laser_frame";
scan.angle_min = -1.57;
scan.angle_max = 1.57;
scan.angle_increment = 3.14 / num_readings;
scan.time_increment = (1 / laser_frequency) / (num_readings);
scan.range_min = 0.0;
scan.range_max = 100.0;
scan.scan_time = (1 / laser_frequency);
scan.ranges.resize(num_readings);
scan.intensities.resize(num_readings);
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < num_readings; ++i){
scan.ranges[i] = ranges[i];
scan.intensities[i] = intensities[i];
}
scan_pub.publish(scan);
++count;
r.sleep();
}
}
- This code creates a publisher with the name fakeScan
- The scan values are being generated inside a
for loop(line 15-18 (excluding the blank lines))
- These scan values are then copied to a LaserScan message (line 20, 32-35)
- The message is being published at line 36. Also, note that the publish rate is 1 Hz (line 12)
As all seems okay we will go ahead and build the project. On the console browse to the catkin_ws directory and then run
$ catkin_make
This should proceed without any errors.
Next, we launch the project with the following command
$ roslaunch beginner_project fakeLaserScan.launch
This also should proceed without any errors.
Now we will open another console from the Tools menu and verify the topics with following commands
$ rostopic list
Outputs :
/fakeScan
/rosout
/rosout_agg
In the result, we see out topic /fakeScan appears. Further, we can check if the topic is publishing the correct information or not with the following command
$ rostopic info /fakeScan
Outputs
Type: sensor_msgs/LaserScan
Publishers:
* /fakeLaserScan (http://10.8.0.1:42942/)Subscribers: None
Thus we verified that the topic is indeed publishing a scan message. Lets load rviz to visualize the data.
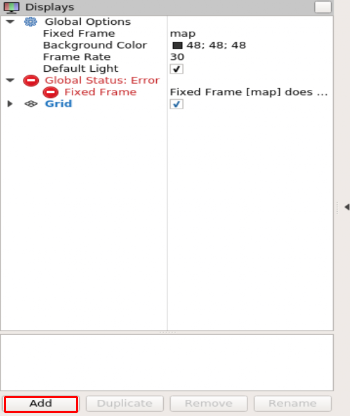
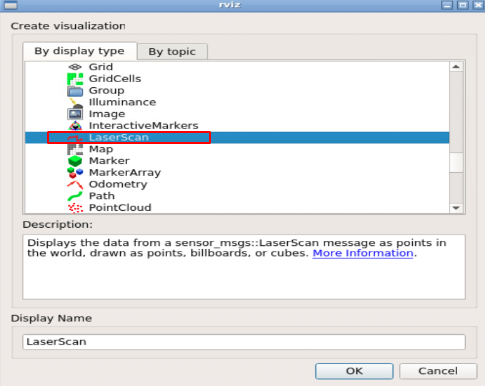
$ rosrun rviz rviz
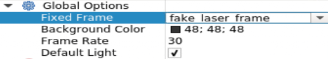
Now we see that there is an error with the frame field.
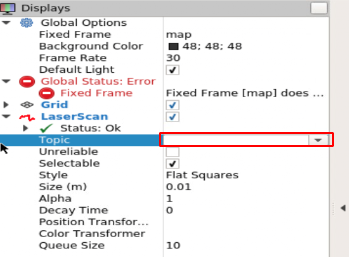
To solve that error we will modify the Fixed Frame field in the Global Option component by writing fake_lasaer_frame in the field (as shown)
- Finally, we have the scan showing up in the visualization panel.
What we did is essentially telling rviz to use the laser_frame for the global fixed frame as well.
This can be done by remapping with the following line of command
$ rosrun tf static_transform_publisher 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 map fake_laser_frame 10
// RELATED LINKS:
* ROS Answers original question: https://answers.ros.org/question/291726/range-sensor-does-not-detect-objects-in-gazebo/
* Robot Ignite Academy: https://goo.gl/vPiuiC
* ROS Development Studio: https://goo.gl/fGnMuv






0 Comments